- Skating on the Flat
- Skating/Adductors
- Snowplough (Centre of Mass)
- Combining Snowplough with Dynamics
- Basic Dynamics (skis parallel)
- Ankle Flex (Anterior Tibialis contraction)
- Everting the Feet
Skating on the flat
Some people simply have no experience of skating so they need to be taught how to skate. Teaching skating is very simple. The skier simply diverges the ski tips very wide bringing the tails almost together. The instructor stands in front – with skis on but held close together and between the diverged tips of the student’s skis. A ski pole is held across the front of his body in two hands. The skier is then asked to grab the pole in the middle and push the instructor backwards. To make this happen the skier has to fall forwards and apply pressure. The inclination forwards pulls the diverged skis both onto their inside edges. Grip is required from the edges and a push from the legs so it helps if the feet are both rolled onto their inside edges (and adductor muscles engaged in both legs) to prevent the skis from flattening and skidding outwards.
The key focus here is to ensure that the ski grips and the centre of mass is displaced. Once the instructor starts to move backwards the skier will accelerate due to the continued pressure, forward inclination and continued pushing with the legs. The sliding forwards will feel safe due to the support in front and so the sensations of skating/sliding and propulsion will be experienced.
The final stage is for the skier to just hold onto the pole but without the instructor there – imagining that the instructor is there and going through all the same motions – pushing the imaginary instructor ahead. This time there is a natural acceleration and skating as a result.
The sensation of both feet being held on their inside edges and of pushing the centre of mass with the legs are fundamental to skiing – or more the “falling forward” of the centre of mass.
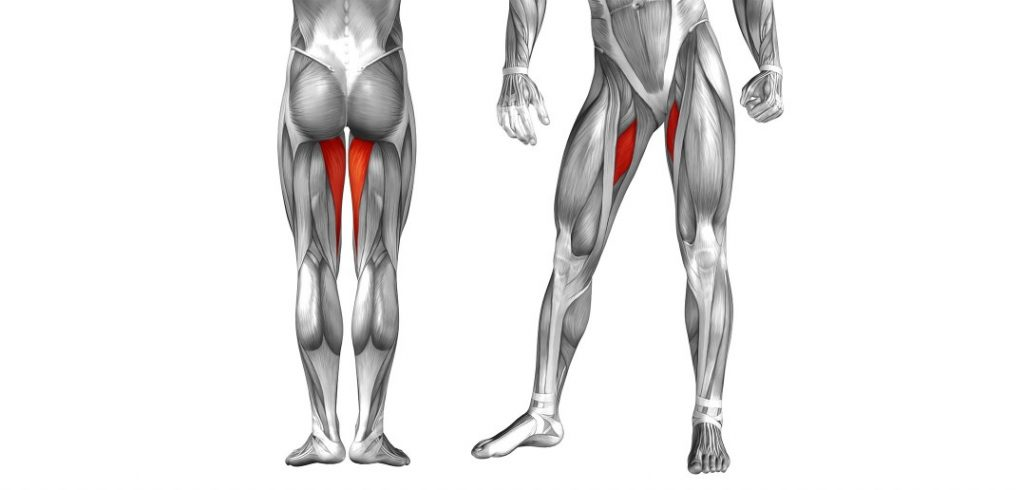
Skating/Adductors
Skiing is just disguised skating. The main difference is the skis are wide and have two edges. When diverging the skis outwards at the tips into a skating stance the skis want to flatten on the snow and the stiff shaft of the ski boots will pull the knees outward. The adductor muscles need to be engaged to hold the skis on their inside edges. This is a pattern of muscle use – the adductors of both legs contracting – that should be maintained when skiing parallel. This is partly dependent on the skier’s morphology. If the femurs are naturally directed inwards less adductor use might be appropriate but if slightly bow legged there may be a need to consciously work the adductors.
Only when snowplough braking should the adductors be released to widen the spreading of the tails of the skis from the hip joints.
The other difference between skis and skates: – it’s just that skis bend and scribe arcs on the ground and are generally used on slopes not flat lakes. Skating actions are fundamental for a skier’s development because they involve independent leg action where only one leg at a time is really used. Although skiers can stand on two feet the body is oriented specifically on one hip joint at a time (when turning) and has to function as if standing on one leg. Skating exercises such as skating step turns are helpful in developing basic skills. Skating turns use diverging skis (opposite from snowplough) and incremental stepping of the centre of mass inward toward the turn centre. This is ideally the first sort of turning that any complete beginner should experience – on flat terrain.
Snowplough (Centre of Mass)
The braking snowplough requires the adductors of both legs to be relaxed to open up the hip joints.
First turns are made by simply tightening the adductors in one leg only – to turn left it’s in the right leg. With narrower ploughs then the adductors of both legs should be engaged.
Weight is always maintained on whatever ski is furthest down the mountain so that it can act as an effective brake. Changes of pressure on any ski are due to geometrical effects between the skis and the slope angle – not “transfer of weight”.
Starting a turn when traversing the slope in a plough requires only a slight movement of the Centre of Mass toward the downhill ski. This ski then slowly feeds the skier into a controlled turn. When facing directly down the fall line, the body being held constantly toward the inside ski in the turn, ensures the outside ski can takeover the completion of the turn. The pressure changes on the skis are automatic – just move the Centre of Mass toward the centre of the intended turn and keep it there from start to finish.
The outside ski in the turn works by “deflection” as it runs forward (extending that leg). The inside ski works by a sideways pivoting action (relaxing and bending that leg).
Combining Snowplough with Dynamics
Dynamics is explained in terms of the mechanics of accelerations. (F=mA Newton’s 2nd Law). In skiing this means you move your centre of mass (either falling or with a push) in the direction you want to turn. You do not transfer your weight to the outside ski as is incorrectly taught in ski schools.
In the Snowplough using dynamics requires the adductors of both legs to be engaged and now the “deflection” is carried out by moving the Centre of Mass (CoM) across the skis in the direction of turning. The displacement of the CoM affects the geometry of both skis with respect to the slope (one goes flatter and the other more on edge) and that’s where the deflection comes from.
On steeper terrain the downhill ski (inside ski of the turn) takes the weight of the body and is used as a brake – pivoting slowly into the turn – until half way through the weight shifts by itself to the outside ski which is now able to take over the continued braking effect.
Basic Dynamics (skis parallel)
- Skis must be travelling forward – like a bicycle
- This is mainly about using the outside leg (start of new turn) to push the centre of mass into the centre of the new turn – for the whole duration of the turn
- There is no “balance” when skiing – dynamics is the physics of disequilibrium
- You are looking for stability from organised accelerations (ski technology!)
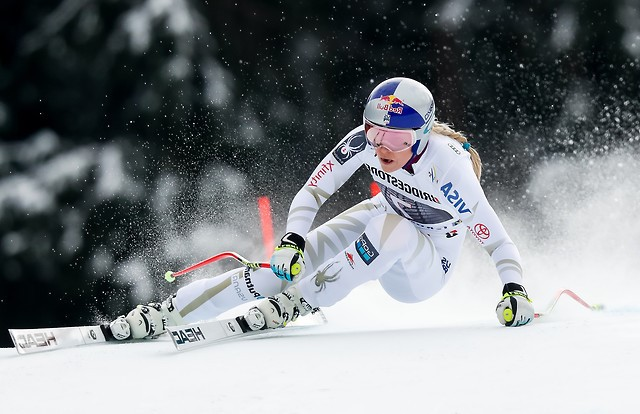
- Notice in the photos below the outside leg is essentially straight in a skating action (flexion for absorption and other purposes is primarily at the hip joint)
- The centre of mass goes down toward the snow – and to complete the turn it comes back up – like a motorbike in a turn
- There is no “Centrifugal Force” acting on the skier – only a deflection inward away from a straight line. This deflection is used to lift the skier up at the end of the turn – which involves “finishing” the turn – I.E. turning almost back up the hill.
- Remain square to the skis (follow the skis around the turn with your body) until you are really comfortable with movement of the centre of mass and clearly aware of moving it.



Ankle Flex (Anterior Tibialis contraction)
One way to increase pressure on the ski fronts is to flex the ankle inside the ski boot – not by squashing the ankle but by lifting the forefoot toward the shin and creating shin pressure on the cuffs of the ski boots. The boots then act as a lever transmitting force to the ski fronts. Gripping on ice requires pressure on the ski fronts and is strongly aided by the (upward) flexed ankle. Turning power comes mainly from the ski fronts – pressure on the tails of a ski makes it travel straight ahead.
Contracting the shin muscle protects the knee joints.
Keeping the ankle flexed (upwards) protects the knee and helps keep pressure on the front of the ski boot – even while extending the leg, everting the foot and skiing on ice.
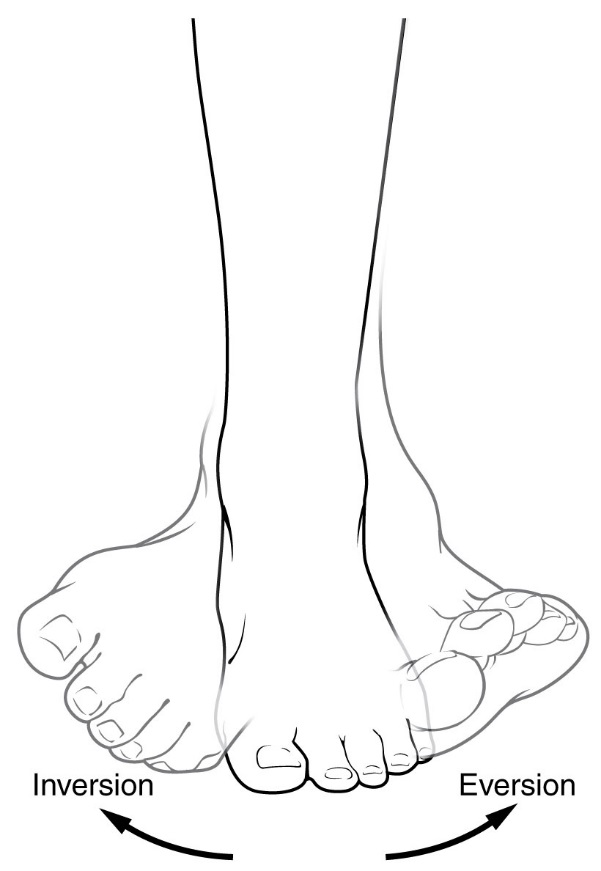
Everting the Feet
When the skis are parallel the feet still “diverge” (as if skating) inside the ski boot – each foot being turned outward (everted). This obviously isn’t visible. This is to combat the tendency to twist the foot inwards to”turn” the ski directly -a mistake which flattens the ski and causes loss of grip.