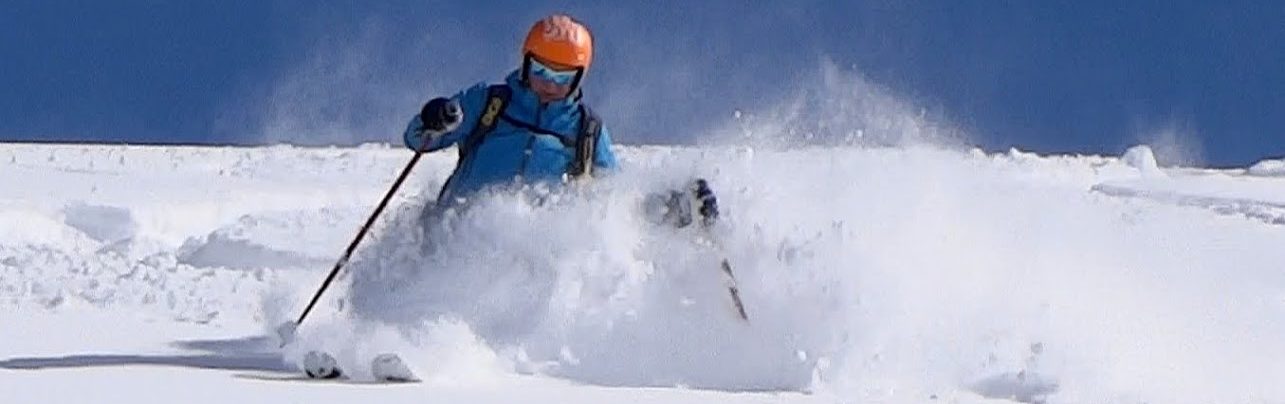
First steps today using dynamics for Tyler and Hannah…
Hannah was compromised from previous ineffective application of snowploughs while holding the adductor muscles tensed – thus forcing her to lean excessively backwards and causing anxiety. In a few days that will hopefully be history.
- Ski Boot Canting
- Skating
- Dynamics
- Pivot
- Combining Dynamics and Pivot
- Feet Forward Technique
- Short Swings
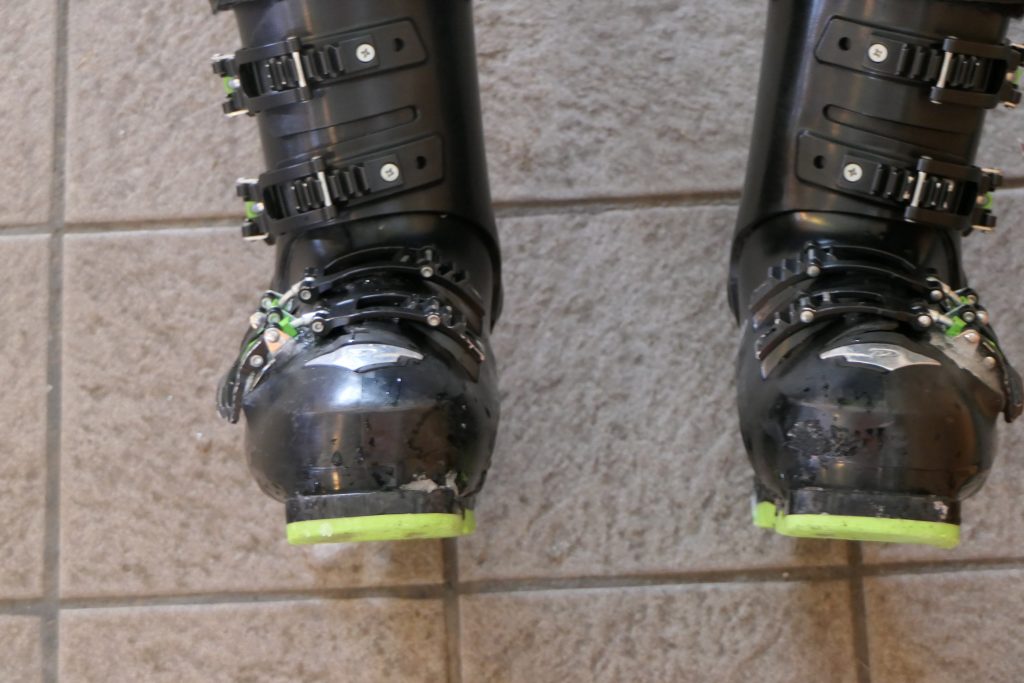
Ski Boot Canting
The canting of the ski boot shaft to match bone structure is critical before working on skating exercises. When the boot soles are not parallel – as with Tyler today – then adjustment is necessary. Fortunately his boots were able to be adjusted. ( legs locked out straight – unweighted (sitting down) – feet hip width apart)

Skating/Adductors
Skiing is just disguised skating. The main difference is the skis are wide and have two edges When diverging the skis outwards at the tips into a skating stance the skis want to flatten on the snow and the stiff shaft of the ski boots will pull the knees outward. The adductor muscles need to be engaged to hold the skis on their inside edges. This is a pattern of muscle use – the adductors of both legs contracting – that should be maintained when skiing parallel.
Only when snowploughing should the adductors be released to widen the spreading of the tails of the skis from this hip joints.
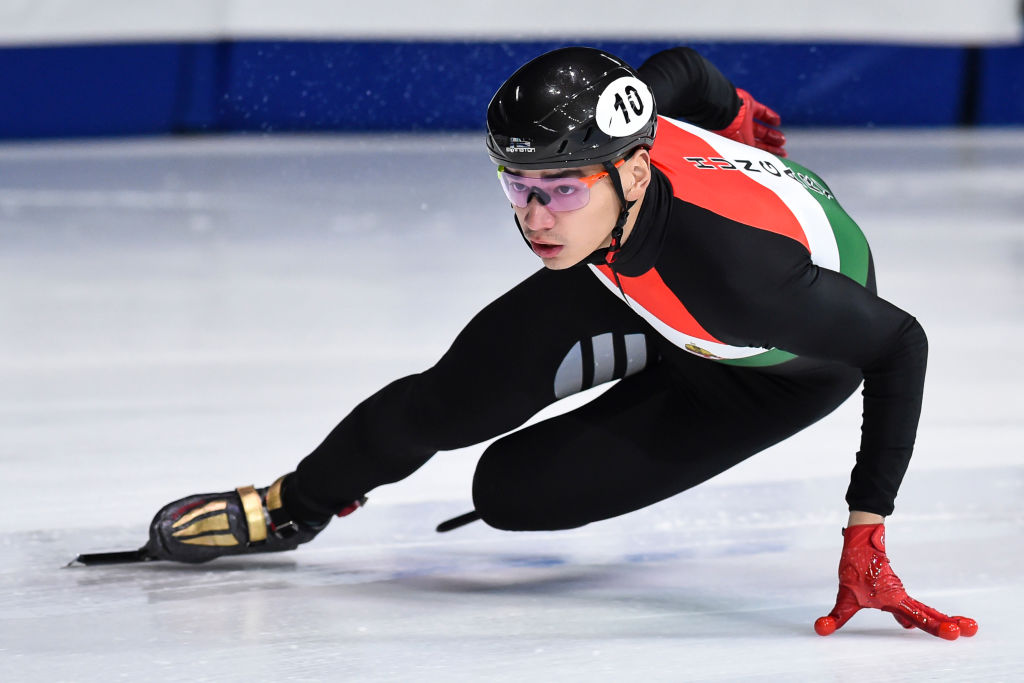
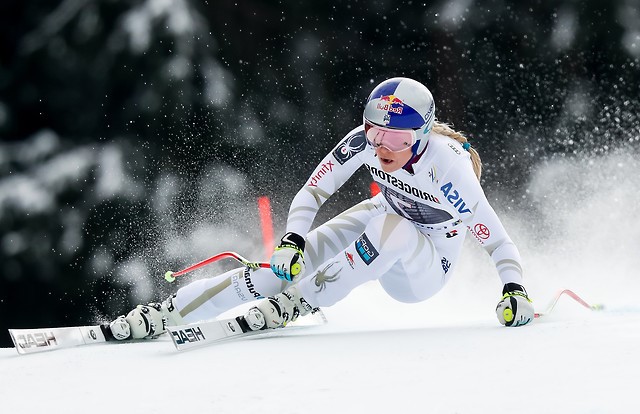
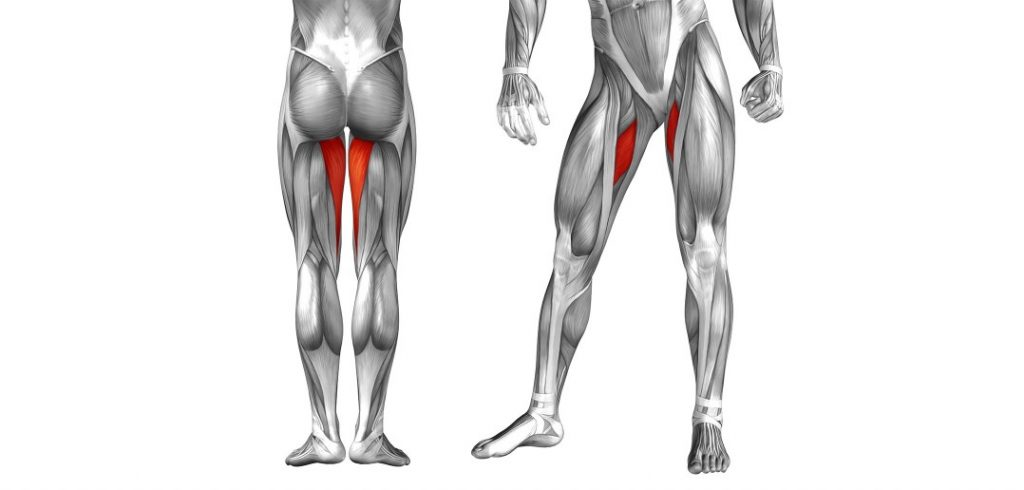


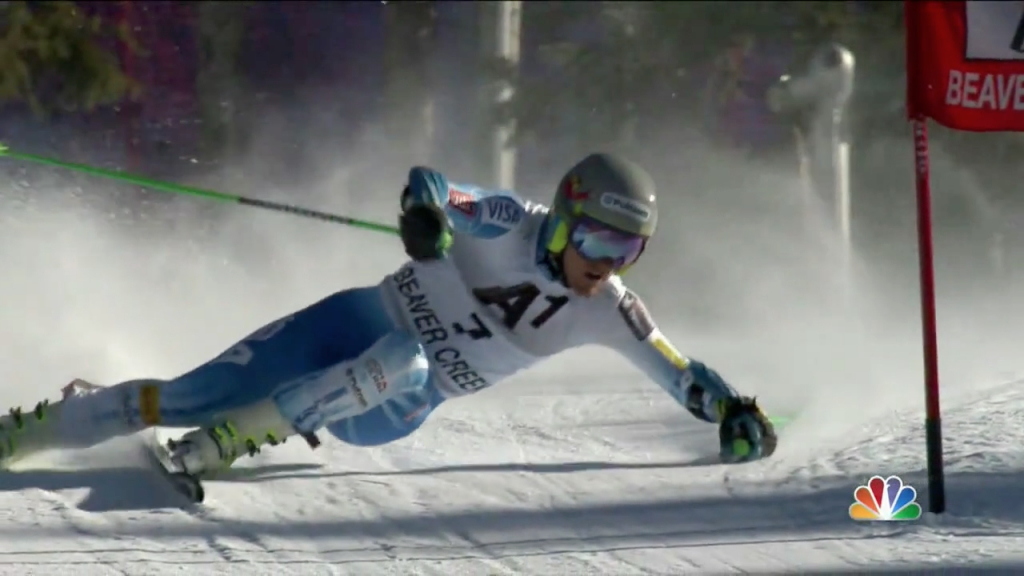
The other difference between skis and skates: – it’s just that skis bend and scribe arcs on the ground and are generally used on slopes not flat lakes. Skating actions are fundamental for a skier’s development because they involve independent leg action where only one leg at a time is really used. Although skiers can stand on two feet the body is oriented specifically on one hip joint at a time (when turning) and has to function as if standing on one leg. Skating exercises such as skating step turns are helpful in developing basic skills. Skating turns use diverging skis (opposite from snowplough) and incremental stepping of the centre of mass inward toward the turn centre. This is ideally the first sort of turning that any complete beginner should experience – on flat terrain.
Basic Dynamics
- Skis must be travelling forward – like a bicycle
- This is mainly about using the outside leg (start of new turn) to push the centre of mass into the centre of the new turn – for the whole duration of the turn
- There is no “balance” when skiing – dynamics is the physics of disequilibrium
- You are looking for stability from organised accelerations (ski technology!)
- Notice in the photos below the outside leg is essentially straight in a skating action (flexion for absorption and other purposes is primarily at the hip joint)
- The centre of mass goes down toward the snow – and to complete the turn it comes back up – like a motorbike in a turn
- There is no “Centrifugal Force” acting on the skier – only a deflection inward away from a straight line. This deflection is used to lift the skier up at the end of the turn – which involves “finishing” the turn – I.E. turning almost back up the hill.
- Remain square to the skis (follow the skis around the turn with your body) until you are really comfortable with movement of the centre of mass and clearly aware of moving it.

Pivot (Skis sliding Sideways)
Pivoting is derived from the skis sliding sideways and can be developed from side slipping (It’s a braking form of turning). With a “pure pivot” as an exercise there is no forward travelling of the ski across the hill. Support for the centre of mass is now provided by support from a downhill pole plant. This is the real reason why we have ski poles! There is a full dedicated explanation of pivoting at the following link: “PIVOT“
Combining Dynamics and Pivot
- Dynamics depends of forward motion of the skis and lateral falling/pushing of the centre of mass
- Pivot depends on lateral motion of the skis – but always with the centre of mass being driven inward (toward the turn centre)
- The two can be combined – when there is both forward and lateral motion – making overall control of trajectory and speed totally under control of the skier
- In all cases there must be active adductor muscle use – and the feet must be “everted” ie. turned outward inside the ski boots – diverging sightly (skating stance)
- The essential element to take from combining pivot and dynamics is to execute the turn transition from the uphill edge of the uphill ski – noting that the ski enters the new turn more easily than when on its inside edge and this also prevents stemming (and body rotation)
Feet Forward Technique
“Feet Forward Technique”… gives security through the start of a turn on steep terrain by tightening the turn radius.
Pushing the outside (uphill initially) foot forward during the turn. The foot never gets in front of the other foot – it just tightens the turn instead.
The exercise is practised with skis off and standing in ski boots. For this static exercise we use ski pole support with the body faced downhill with the uphill foot pointing across the hill and the downhill foot pointing downhill and the heel jammed into the snow. The uphill boot is pulled over onto its inside edge and pushed forwards in a natural arc.
Here is some video of exactly the same action in ice hockey training. In skiing the direction of travel would be straight downhill instead of straight ahead on the flat ice.
Short Swings
We worked a little bit on Short Swings to encourage the active use of weighting the ski poles (downhill) for controlled dynamics and sideways action of the skis.

